

TCP/IP Control Panel – Info or User Mode/Advanced
The table below summarises options for finding a computer’s MAC address. Here are the OUI for other some well-known manufacturers.
Ethernet mac address format serial number#
The second half ( 24 MORE BITS) of a MAC address represents the serial number assigned to the adapter by the manufacturer.įor example, consider a network adapter with the MAC address “00-A0-C9-01-23-45.” The OUI for the manufacture of this router is the first three octets-”00-A0-C9″ – In this case Intel corporation. These IDs are regulated by an Internet standards body (see sidebar). The first half ( 24 BITS) of a MAC address contains the ID number of the adapter manufacturer.

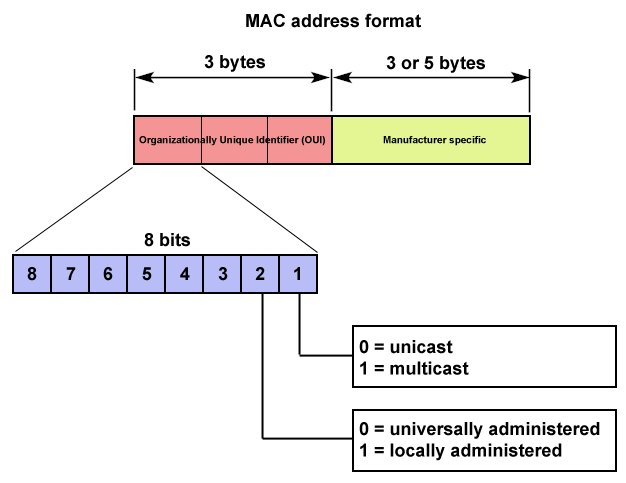
MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS or MMMM-MMSS-SSSS format By convention, MAC addresses are usually written in one of the following formats: Let’s try to understand the MAC address format with the help of the image given below.Īs shown in the above diagram, MAC addresses are 12-digit hexadecimal numbers (48 bits in length). All three numbering systems use the same format and differ only in the length of the identifier. This 48-bit address space contains potentially 281,474,976,710,656 possible MAC addresses. The original IEEE 802 MAC address comes from the original Xerox Ethernet addressing scheme. HOW MANY MAC ADDRESSES CAN THERE BE IN THE WORLD? The ARP takes data from an IP address through an actual piece of computer hardware. It is hardwired or hard-coded onto your computer’s network interface card (NIC) and is unique to it.ĪRP (Address Resolution Protocol) translates an IP address into a MAC address. The MAC address is sometimes referred to as a networking hardware address, the burned-in address (BIA), or the physical addressĪ MAC address is given to a network adapter when it is manufactured. It contains the error detection information.The MAC address is used by the Media Access Control sublayer of the Data-Link Layer (DLC) of telecommunication protocols.Įvery NIC (also called LAN card) has a hardware address that’s known as a MAC, for Media Access Control. Padding − This is added to the data to bring its length to the minimum requirement of 46 bytes.ĬRC − CRC stands for cyclic redundancy check. The maximum size of data field is 1500 bytes. In case of IEEE 802.3, the field is length that stores the number of bytes in the data field.ĭata − This is a variable sized field carries the data from the upper layers. In case of Ethernet (DIX), the field is type that instructs the receiver which process to give the frame to. Source Address − It is a 6 byte field containing the physical address of the sending station. Start of Frame Delimiter (SOF) − It is a 1 byte field in an IEEE 802.3 frame that contains an alternating pattern of ones and zeros ending with two ones.ĭestination Address − It is a 6 byte field containing physical address of destination stations. In case of Ethernet (DIX) it is an 8 byte field and in case of IEEE 802.3 it is of 7 bytes. Preamble − It is the starting field that provides alert and timing pulse for transmission. The main fields of a frame of classic Ethernet are − The frames of the two standards are very similar except for one field. Frame Format of Classic EthernetĬlassic Ethernet frames can be either of Ethernet (DIX) or of IEEE 802.3 standard. In MAC sublayer, the frame formats for the Ethernet data frame are laid down.Ĭlassic Ethernet was first standardized in 1980s as IEEE 802.3 standard. In the physical layer, the features of the cables and networks are considered. It provides data rates between 3 to 10 Mbps.It operates both in the physical layer and in the MAC sublayer of the OSI model. Classic Ethernet is the original form of Ethernet used primarily in LANs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
